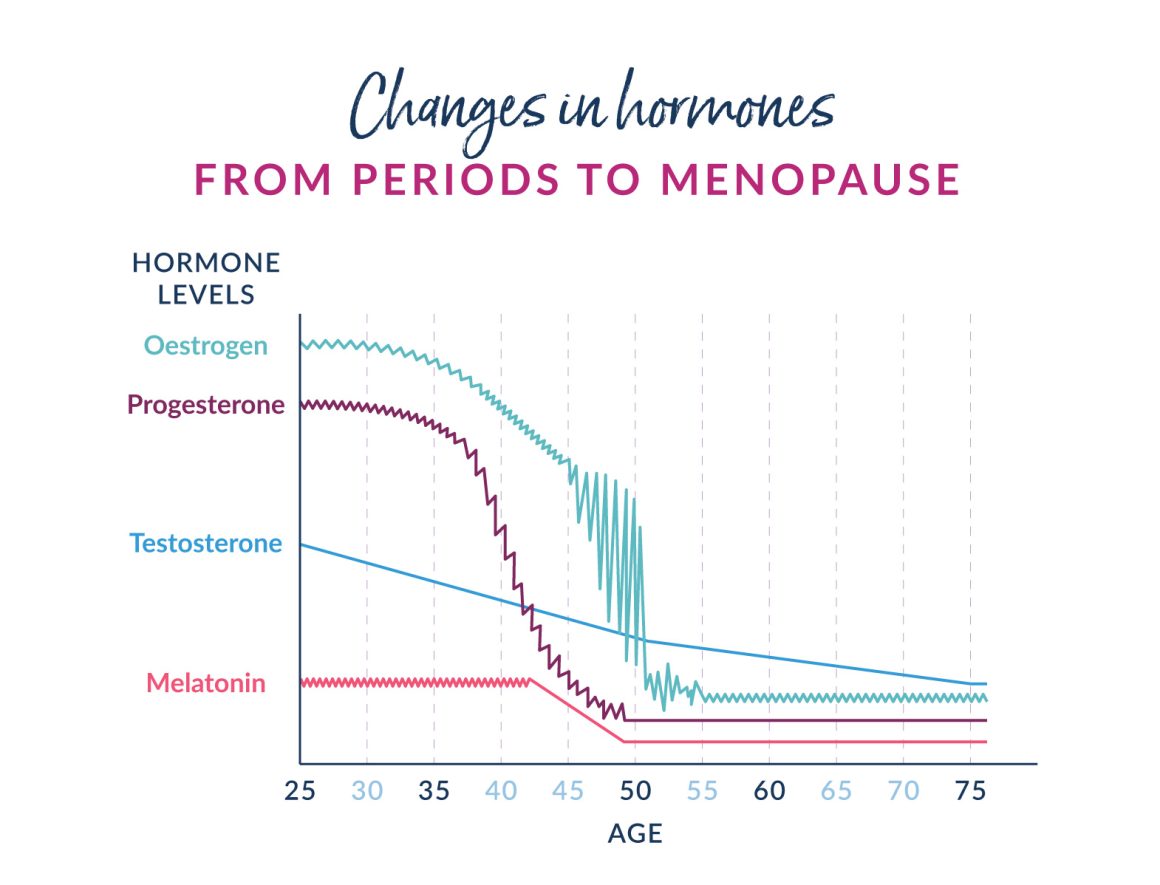
Women and people with periods experience both physical and emotional changes as they approach menopause. During this time, the ovaries gradually stop producing oestrogen and progesterone – the hormones responsible for the menstrual cycle – causing periods to become irregular before eventually stopping. Menopause can also bring a range of symptoms including mood swings, hot flashes, and sleeplessness.
While the menopause is a natural part of ageing, hormonal fluctuations can make it a challenging transition, impacting both the body and overall well-being. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is one treatment used to relieve symptoms of the menopause, and thanks to growing awareness of menopause symptoms and treatments, its popularity has increased in recent years. But how does HRT work, and what should you know about it?
What Is HRT and How Does It Work?
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a medical treatment to replace the hormones that decline during the menopause. It’s also used to manage symptoms of medically induced menopause, treat hypogonadism (a condition in which the body does not produce enough hormones), and other menstrual conditions. Throughout the perimenopause, the time before the menopause, the ovaries gradually stop the production of oestrogen and progesterone. These hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, ovulation and pregnancy, but they also play a key role in maintaining bone density and overall wellbeing. The decline of these hormones can lead to symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, and increased risk of osteoporosis to name but a few.
To replace these hormones, there are different types of HRT available:
- Combined HRT (oestrogen and progesterone): The most common type, prescribed to those who still have a womb.
- Oestrogen-only HRT: Recommended for individuals who have had a hysterectomy, as they no longer need progesterone to protect the uterus lining.
HRT comes in various forms, including tablets, skin patches, gels, and sprays. The right type and method depends on individual needs, so it is important to consult a doctor to determine the most suitable option.
HRT and Periods: What to Expect
HRT can affect periods differently depending on the type of treatment and what stage of menopause you are at. Some people may experience irregular bleeding, or withdrawal bleeding, while others may stop having periods entirely.
- Sequential combined HRT: This type contains both oestrogen and progesterone but follows a cycle – oestrogen is taken every day, and progesterone for 10-14 days of each 28-day cycle. It is typically offered to individuals who are still having periods but are suffering with their menopausal symptoms. A withdrawal bleed usually occurs at the end of each progesterone course, similar to a period. This will be more familiar if someone has taken contraceptive pills in their earlier life.
- Continuous combined HRT: In this method, both oestrogen and progesterone are taken every day without breaks. It is recommended for those who are postmenopausal (have not had a period for more than one year).
Irregular bleeding is common in the first few months of taking HRT and usually settles within 6 months. However, you should speak to your doctor if bleeding continues beyond 6 months, becomes heavy or is painful.
Benefits of HRT
For many, HRT can be life-changing, with its benefits often outweighing the risks and side effects. Prescriptions of HRT have surged in recent years, driven by the so-called ‘menopause revolution’, increased awareness and a better understanding of its safety.
The key HRT benefits include:
- Relief from menopause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, mood swings and anxiety. HRT improves the overall quality of life for a lot of women and those with a uterus.
- Preventing osteoporosis, the thinning of bones which is common after the menopause due to low levels of oestrogen.
- Helps maintain muscle strength, which tend to weaken as you reach the menopause.
Is HRT Safe?
Like any medical treatment, HRT has potential risks and side effects, though they are generally low for most people.
Common HRT side effects (usually temporary) can include:
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
Other potential risks can include:
- Breast cancer: Long-term use of combined HRT is associated with a small increased risk of breast cancer. Research suggests that for every 1,000 women taking combined HRT for five years, there may be around five additional cases of breast cancer. If you have a history of breast cancer, or there is in your family that you know about, it’s important to discuss this with your healthcare professional if you’re considering HRT.
- Blood clots: There is a slightly increased risk of blood clots with some types of HRT, particularly the oral tablets.
However, these risks depend on factors such as personal health history, the type of HRT taken, and how long you have been taking it for. Your doctor can help assess the benefits and risks based on your individual circumstances and family history, if known.
Is HRT Right for You?
If you are experiencing severe menopause symptoms that affect your daily life, or you are concerned about your bone health, it may be worth discussing HRT with your doctor. HRT is not the right choice for everyone, but for many, it provides significant relief from menopause symptoms and helps support long term health. Weight resistance training, healthy lifestyle and calcium supplements can help mitigate some health concerns but won’t affect severe menopausal symptoms.
Additionally, a quick final note for vegans and vegetarians, some commonly prescribed forms of HRT contain animal derived ingredients. For example, certain types of micronised progesterone contain gelatine, making them unsuitable for those following a strictly plant-based lifestyle. Fortunately, vegan and vegetarian-friendly alternatives exist in the form of vaginal pessaries or gels. Menopause shouldn’t have to be a struggle.












